Organizations are advancing their efforts, investing in OT cybersecurity programs
ICS cybersecurity threats remain high and present evolving challenges, a new SANS report reveals.

However, since the last SANS OT/ICS report released in 2017, a growing majority of organizations have significantly matured their security postures over the last two years and are adopting strategies that address OT/IT convergence.
“The findings in this latest SANS report make it clear that 2019 is the year for ICS cybersecurity,” said Nozomi Networks CEO Edgard Capdevielle.
“We see the urgency and growing demand every day as more and more industrial companies around the world reach out to us for help in aggressively arming themselves against cyber threats rising in number, persistence and strength. ICS cybersecurity is a priority and organizations are strengthening their cybersecurity posture with innovative OT security technologies that provide deep visibility and control across OT and IT.”
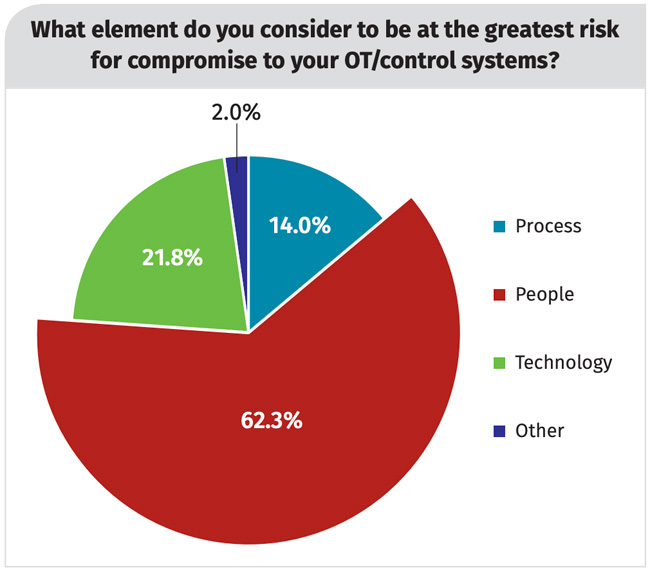
ICS cybersecurity risk remains high
Half of this year’s respondents rate their ICS security threat as high or severe. While down significantly from 2017, it is still a daunting number that reinforces the fact that even as organizations make OT cybersecurity a priority, cyber attacks and data breaches continue to rise and are evolving as OT and IT converge and organizations adopt mobile and wireless capabilities.
- 50% of respondents rank ICS security threats high or severe/critical – down from 69% in 2017.
- 62% identify people (internal and external) as the greatest risk for compromise.
- 61% of all incidents had a disruptive effect on OT activities.
- Unprotected devices, nation-states/hactivisits and internal accidents rank as the top three threats, followed by IT integration and external (supply chain or partner) threats.
- Less than 25% of respondents worry about phishing scams, despite continued evidence from ICS attack research that this tactic continues to be a favored mechanism to establish an initial point of compromise and entry into many industrial control systems in IT.
ICS cybersecurity postures are maturing
This year’s survey found most organizations are now taking ICS threats seriously and are making solid progress in maturing their security postures.
- 42% saw their control system security budget increase over the past two years (vs. 29% in 2017).
- 69% have conducted a security audit of their OT/control systems or networks in the past year.
- 60% now proactively depend on trained staff to search out events, up 23% from 2017.
- 62% have a well-defined (documented) system perimeter or boundary for their OT/control systems.
- 51% are using continuous active monitoring to detect vulnerabilities.
- 44% now use anomaly detection tools to identify trends (up 9% from 2017).
- 45% say they are now detecting compromise within 2-7 days of the incident. 53% of those say they move from detection to containment within 6 to 24 hours.
- 46% say increasing visibility into control system cyber assets and configurations is a 2019 priority.
- 28% say implementing anomaly and intrusion detection tools on ICS networks is a 2019 priority.
OT/IT convergence is the norm
This year’s survey found most organizations now embrace OT/IT convergence – while there’s still much to do as organizations work to align their corporate priorities and maintain their budgets.
- 65% say the current OT/IT collaboration level is moderate or better.
- 54% say the CISO/CSO establishes security policy around OT assets while, for 42%, the IT manager bears primary responsibility for implementation of the related controls.
- 60% of organizations first consult a variety of internal resources when signs of an infection or infiltration of their control system cyber assets or network are detected.
- 84% either have implemented, are implementing or plan to implement a strategy to address OT/IT convergence.
- 30% say investing in general cybersecurity awareness programs for employees including IT, OT and hybrid IT/OT personal is a top priority for 2019.
- 27% say bridging IT and OT initiatives is a top priority for the year.
Mobile and wireless – the underestimated threat
Cybersecurity challenges are expanding as ICS boundaries become broader, interwoven and interdependent, exchanging information with myriad other systems and processes. Challenges in this area include mobile and wireless devices, which respondents give a low level of risk.
The report points out that some mobile applications replace engineering workstation applications, and they should treat their risk at a higher level. Also, wireless communication is becoming more widely used to transfer data from sensor networks. This further increases the attack surface and opens an organization up to severe consequences if compromised.
- 37% of OT control system connections are wireless (public or private cellular, satellite or radio), yet respondents did not rate wireless communications and protocols as subject to high risk or impact.
- More than 40% of respondents are using cloud-based services for a number of OT/ICS system functions.
- One out of six respondents use cloud-based services for “control system application virtualization, including remote logic,” lending to the growing importance and dependence on cloud services.
- Mobile devices (laptops, tablets and smart phones) that replace or augment traditional desktops or fixed systems are among the top 5 technology risk areas for OT control systems, however respondents consider them to have a low level of impact (almost last).