Your employees uploaded over a gig of files to GenAI tools last quarter
In Q2 2025, Harmonic reviewed 1 million GenAI prompts and 20,000 uploaded files across more than 300 GenAI and AI-powered SaaS apps, and the findings confirm that sensitive data is being exposed through GenAI tools, something many security leaders fear but find difficult to measure.
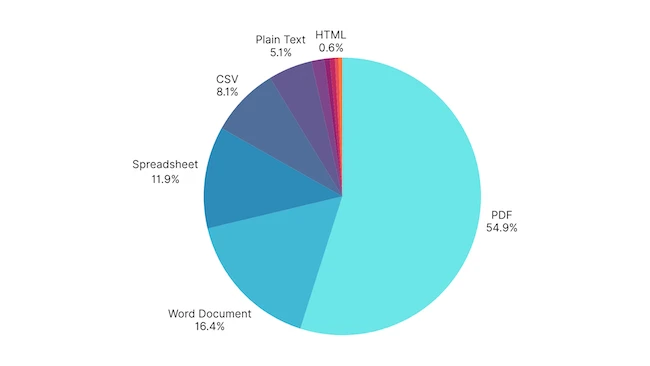
Distribution of file types uploaded to GenAI tools in Q2 2025 (Source: Harmonic Security)
Enterprises use 23 New GenAI tools per quarter on average
Of these numbers, 22% of files and 4.37% of prompts contain sensitive information, this includes source code, access credentials, proprietary algorithms, M&A documents, customer or employee records and internal financial data.
In just Q2, the average enterprise saw 23 previously unknown GenAI tools newly used by their employees, stretching security teams which need to ensure each tool is properly vetted and reviewed. A high proportion of AI use comes from personal accounts which may be unsanctioned and / or without safeguards. Some 47.42% of sensitive uploads to Perplexity were from users with standard (non-enterprise) accounts, although these numbers improve for ChatGPT where 26.3% is via personal accounts, and just 15% of Google Gemini use via personal accounts.
Enterprises upload over 1GB of files monthly
Of all sensitive prompts analyzed in Q2, 72.6% originated in ChatGPT, followed by Microsoft Copilot, Google Gemini, Claude, Poe, and Perplexity. One dominant trend stands out: code leakage was the most common type of sensitive data sent to GenAI tools and was especially prevalent in ChatGPT, Claude, DeepSeek and Baidu Chat.
The average enterprise uploaded 1.32GB of files in Q2 with PDFs accounting for half. However, a full 21.86% of these files contained sensitive data with a disproportionate concentration of sensitive and strategic content compared to prompt data. For instance, files were the source of 79.7% of all stored credit card exposures, 75.3% of customer profile leaks, and 68.8% of employee PII incidents, all categories with high regulatory or reputational risk. Even in financial projections, where both channels are active, files edged out prompts with 52.6% of total exposure volume.
How common SaaS apps expose sensitive content to GenAI
Not all GenAI risk comes from obvious chatbots. A growing share now stems from everyday SaaS tools that quietly embed LLMs and train on user content which are not flagged as GenAI tools by most enterprise controls. Yet they often receive sensitive content. For instance, Canva was used to create documents containing legal strategy, M&A planning, and client data. Replit and Lovable.dev handled proprietary code and access keys whilst Grammarly and Quillbot were used for editing contracts, client emails, and internal legal language.
Employees upload sensitive data to unsanctioned Chinese GenAI tools
Chinese GenAI tools are becoming popular in Western companies. Although these platforms are mostly unsanctioned, developers use them because they are fast, effective, and free.
Research found that many employees use these tools to upload sensitive information, including source code, financial data, and personal records. Each tool carries its own unique risks, for example, Baidu Chat often leaked legal and payment documents, while DeepSeek exposed credit card and employee information.
These GenAI platforms usually offer little transparency or control, yet employees continue to use them with little resistance.