High-impact IT outages cost businesses $2 million per hour
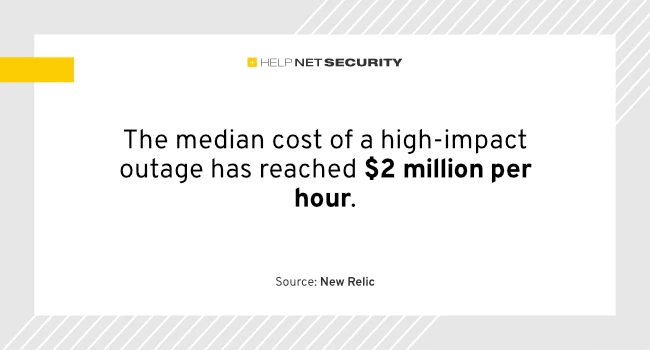
The financial stakes of downtime are climbing, and IT leaders are being pushed to rethink how they monitor complex systems. According to the 2025 Observability Forecast from New Relic, the median cost of a high-impact outage has reached $2 million per hour. Organizations with full-stack observability cut that cost in half, showing the tangible business benefits of stronger monitoring practices.
AI adoption reshapes monitoring
AI has moved beyond experimental projects. The survey found that 54% of organizations now use AI monitoring in production, up from 42% last year.
Executives rank AI-assisted troubleshooting as the most impactful use case, followed closely by automatic root cause analysis, predictive analytics, and automated remediation like rollbacks or configuration changes. These tools help IT teams reduce mean time to resolution and contain the impact of incidents.
The report also warns of a growing dependency on AI systems that are themselves complex and opaque. LLM-powered applications and agentic AI often fail in ways that traditional monitoring cannot capture. Dependencies across APIs, pipelines, and downstream applications make failures harder to map. For some organizations, this means deploying AI to monitor AI, using real-time analytics to ensure that new models behave as expected.
AI adoption is now driving the demand for deeper observability, not the other way around. Executives named AI as the top reason they are expanding observability, ahead of security, cost control, or cloud-native development. Leaders who move early on AI-powered observability will be better positioned to catch hidden issues, avoid silent failures, and maintain resilience as AI-driven applications scale.
“Despite the promise of AI to speed application production, the data reveals engineering teams are still losing a third of their time battling issues that are difficult to pinpoint. Full-stack observability can halve the cost of a major outage while speeding up detection and resolution, freeing up teams to focus on innovation that meets business objectives,” said New Relic CEO Ashan Willy.
The cost of outages
Outages now threaten revenue, customer trust, and brand reputation. Survey respondents reported that annual exposure from high-impact outages can reach $76 million, showing why downtime is now a board-level concern.
Organizations with full-stack observability limit both the frequency and impact of outages. They detect problems faster, experience fewer high-impact incidents, and reduce costs, freeing teams from the fire-drill cycles that consume valuable engineering time.
Consolidation gains momentum
Tool sprawl remains a drag on observability maturity. The average organization uses 4.4 tools, down from six two years ago. Despite progress, silos persist. Over half of leaders plan to consolidate onto unified platforms in the next 12 to 24 months.
The driver is both financial and operational. Multiple tools create overlapping costs, integration overhead, and slower response during incidents. By reducing the number of platforms and unifying data flows, teams can accelerate resolution and cut maintenance costs.
Return on observability investment
Seventy-five percent of organizations report positive returns from observability investments, with nearly one in five seeing returns three to ten times the cost. Benefits include reduced downtime, higher operational efficiency, and better customer experience.
For executives, reduced unplanned downtime ranked as the top benefit, while practitioners pointed to less alert fatigue and faster troubleshooting. Both groups saw collaboration across teams improve as visibility expanded.
Obstacles remain
Many organizations still learn about outages from customers or manual checks, with 41% of leaders reporting that tickets or complaints alert them before automated detection.
Complex technology stacks and siloed data remain the main barriers to maturity. Thirty-six percent cite system complexity, and 29% cite too many monitoring tools or fragmented data. Without end-to-end visibility, engineers piece together incidents from partial data, slowing resolution and increasing costs.