Notepad++ secures update channel in wake of supply chain compromise
Notepad++, the popular text and source code editor for Windows whose update mechanism was hijacked last year, has been updated to prevent similar attacks in the future.
Security hardening of Notepad++
The hijacking of the update mechanism was confirmed earlier this month by Notepad++ maintainer Don Ho.
The attackers were able to intercept communications between the updater client and the Notepad++ update servers, allowing them to deliver and run a malicious update in place of a legitimate one.
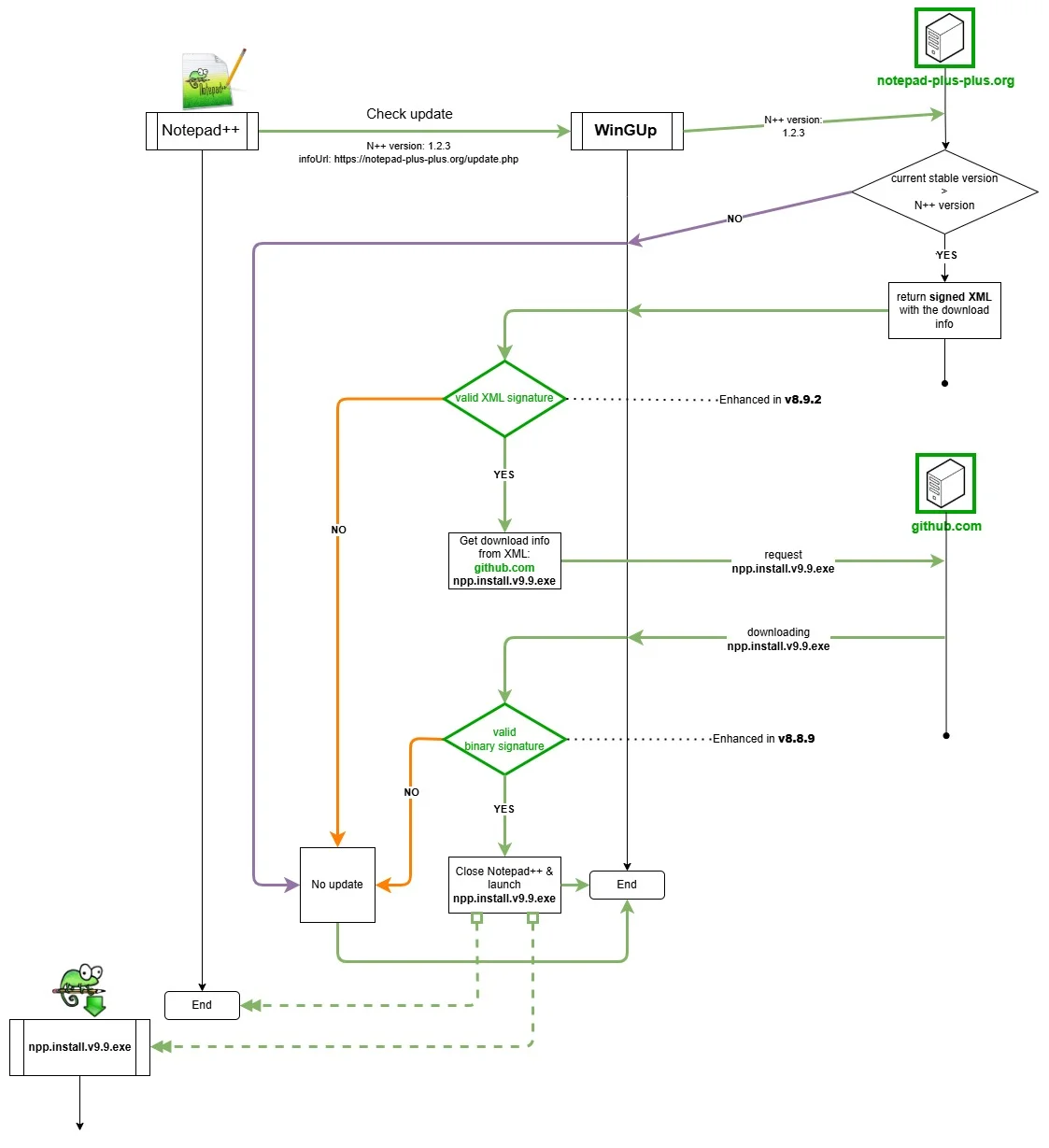
The attack took advantage of several weaknesses:
- Before Notepad++ v8.8.8 (released on November 18, 2025), the XML file containing the download URL for the update was not signed, which allowed attackers to make the software’s auto-updater (WinGUp) download an update from a domain that’s not Notepad++’s GitHub repository
- Before Notepad++ v8.8.9 (released on December 9, 2025), WinGUp would not verify the code signing certificate and validate the signature on the downloaded installer before starting the update
With Monday’s release of Notepad++ v8.9.2, the maintainer has implemented verification of the signed XML file that instructs the updater where to look for the update, thus finalizing the security hardening started in v8.8.8.
The security enhancements of the update process introduced in v8.8.9 and v8.9.2 (Source: Notepad++)
According to Ho, the verification of the signed XML and of the signed installer downloaded from github.com has made the Notepad++ update process “effectively unexploitable.”
Alongside this major hardening, WinGUp has been further strengthened by removing the libcurl.dll dependency to eliminate DLL side-loading risk, disabling two insecure cURL SSL options, and restricting plugin management execution to programs signed with the same certificate as WinGUp.
All Notepad++ users should upgrade to this latest version as soon as possible.
Would-be users are urged to download the software only from the software’s official GitHub repository or from the software’s official page, because fake downloads of Notepad++ from spoofed Notepad++ websites are commonly used by cybercriminals to distribute a variety of malware.
The Notepad++ supply chain compromise
Notepad++’s supply chain compromise happened in June 2025, when the software project’s shared hosting server was hacked.
The attackers lost access to it in early Septemeber 2025, when its kernel and firmware were updated, but they had the credentials for the project’s internal services on that server until early December 2025.
Rapid7 and Kaspersky researchers analyzed the malicious update and execution chains mounted in the interim by the attackers, and found that they resulted in the installation of Cobalt Strike Beacon payloads and/or the Chrysalis bakcdoor to establish command and control communication.
While it was initially believed that the attackers only targeted organizations in Southeast Asia and South America, Palo Alto Networks discovered that organizations in the US and Europe also received malicious updates.

Subscribe to our breaking news e-mail alert to never miss out on the latest breaches, vulnerabilities and cybersecurity threats. Subscribe here!